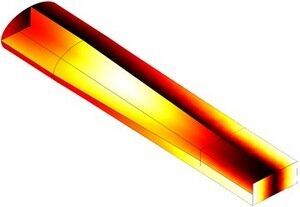
Waveguide Adapter
This is a model of an adapter for microwave propagation in the transition between a rectangular and an elliptical waveguide. Such waveguide adapters are designed to keep energy losses due to reflections at a minimum for the operating frequencies. To investigate the characteristics of the adapter, the simulation includes a wave traveling from a rectangular waveguide through the adapter and into an elliptical waveguide. The S-parameters are calculated as functions of the frequency. The involved frequencies are all in the single-mode range of the waveguide, that is, the frequency range where only one mode is propagating in the waveguide.
...more
Vacuum Flask
The following example solves a pure conduction and a free-convection problem in which a vacuum flask holding hot coffee dissipates thermal energy. The main interest is to calculate the flask's cooling power; that is, how much heat it loses per unit time.Using heat transfer coefficients to describe the thermal dissipation, Modeling the buoyancy-driven flow of air outside the flask to describe the convective cooling.
...more
UHFf Tag
UHF RFID tags are widely used for identifying and tracking animals. This model simulates a passive radio-frequency identification (RFID) tag for the UHF frequency range. With respect to the chip transponder’s complex impedance, a reflection coefficient is computed. This is done using an approach that differs from the conventional scattering parameter analysis method by a real reference impedance value.
...more
Tilted Pad Bearing
Tilted pad thrust bearings are used in rotating machineries with high thrust loading. The thrust load is transferred from a sliding part to a stationary part through hydrodynamic oil films. The tilted pad thrust bearing consists of a series of flat surfaces sliding over stationary tilted pads. The space between the flat surface and the tilted pad is filled by a lubricant that is drawn in due to the sliding motion of the flat surface. The pressure developed in the lubricant in between the sliding surface and the tilted pad counteracts the external load applied to the sliding surface and thus prevents contact between the two surfaces. Integration of the pressure values on the surface of the tilted pad gives the total load on the tilted pad. This total load is used to analyze elastic deformation of the tilted pad. In this model, Reynolds equation is used to calculate the pressure in the film and structural analysis is performed to find the elastic deformation of the tilted pad.
...more
Surface-Mounted Resistor
The drive for miniaturizing electronic devices has resulted in today’s extensive use of surface-mount electronic components. An important aspect in electronics design and the choice of materials is a product’s durability and lifetime. For surface-mount resistors and other components producing heat it is a well-known problem that temperature cycling can lead to cracks propagating through the solder joints, resulting in premature failure. electronics in general there is a strong interest in changing the soldering material from lead- or tin-based solder alloys to other mixtures. This multiphysics example models the heat transport and structural stresses and deformations resulting from the temperature distribution using the Heat Transfer in Solids and Solid Mechanics interfaces.
...more
Static Mixer
In static mixers, also called motionless or in-line mixers, a fluid is pumped through a pipe containing stationary blades. This mixing technique is particularly well suited for laminar flow mixing because it generates only small pressure losses in this flow regime. This example studies the flow in a twisted-blade static mixer. It evaluates the mixing performance by calculating the trajectory of suspended particles through the mixer. The model uses the Laminar Flow and Particle Tracing for Fluid Flow interfaces.
...more
Spiral Tube
A frequently occurring geometry for heat exchangers is that of a long tube wound into a helix or spiral around a core volume. There is to be heat exchange between the tube and the gases (or solids) in the core. However, the length scales of these two parts of the geometry are very different, thus complicating the interface between the tube and the core processes. the tube is too long for direct numerical modeling. Therefore, in the present work, we use an axis-symmetric numerical model of the core and link it to analytical equations for the tube. In this way, radial boundary conditions at the core perimeter become the driving force for the thermal process in the tube; at the same time, the results of the analytical integration in the tube provide boundary conditions for the core. Also, it is shown that there is enhanced convective heat transfer in the curved tubes, compared to straight tubes.
...more
RF Module
Designers of RF and microwave devices need to ensure that the electromagnetics simulations are reliable and robust. Traditional electromagnetic modeling lets you examine RF physics alone, but no real-world product operates under just one branch of physics. To see how other physics phenomena affect the design, you need multiphysics modeling, which allows you to extend the model to include effects such as temperature rise, structural deformations, and fluid flow.
...more
RF Coil
RF coils are important in numerous applications ranging from wireless technology to MRI scanning equipment. This introductory tutorial model demonstrates how to find the fundamental resonance frequency of an RF coil as well as how to perform a frequency sweep to extract the coil's Q-factor.
...more
Reciprocating Engine
The High-Cycle Fatigue of a Reciprocating Piston Engine model is based on an example of a three-cylinder reciprocating engine from the Multibody Dynamics Module. In this engine, a flywheel is mounted on the crankshaft, with the assembly supported on both ends by journal bearings. The model also features three sets of cylinders, pistons, and connecting rods that are identical. Hinge joints are used to connect the bottom ends of the connecting rods to the common crankshaft as well as to connect the pistons to the top ends of the rods. A prismatic joint is used to connect each of the cylinders to a piston.
...more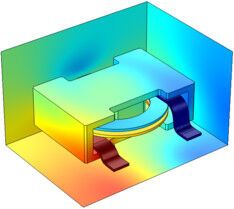
Power Inductor
Power inductors are a central part of many low-frequency power applications. They are, for example, used in the switched power supply for the motherboard and all other components in a computer. Computer simulations are necessary in the design of such inductors. This model calculates the inductance from specified material parameters.
...more
Piezoelectric Devices
Piezoelectric devices contain materials where electric charge is created due to mechanical stress. The presentations, posters, and papers on this page describe multiphysics simulation for devices such as sensors, controllers, and gyroscopes, and applications such as energy harvesting.
...more
Permanent Magnet Generator
This tutorial shows how to model the tubular permanent magnet generator in 2D axisymmetry. The generator consists of a modular stationary stator and movingoscillating slider. The stator is made of three-phase multiturn windings and an iron core. The slider is made of permanent magnets and iron spacers. The open circuit voltage in the three-phase stator windings due to the periodic motion of the slider is calculated.The model is set up using the Magnetic Fields and Moving Mesh physics interfaces. The linear periodicity of the tubular generator is set up manually using the General Extrusion feature.
...more
Permanent
As an example of a magnetostatic problem, consider how to model a horseshoe-shaped permanent magnet. One way is to treat the entire magnet as a ferromagnetic material, where the two end sections are defined as being pre-magnetized in different and opposite directions.
...more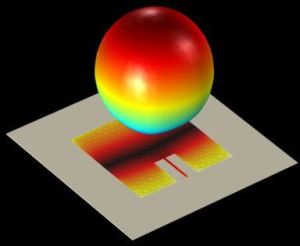
Patch Antenna
The microstrip patch antenna is used in a wide range of applications since it is easy to design and fabricate. The antenna is attractive due to its low-profile conformal design, relatively low cost and very narrow bandwidth. It is known that the antenna impedance will be higher than an accepted value if fed from the edge, and lower if fed from the center. Therefore, an optimum feed point exists between the center and the edge. This model uses an inset feeding strategy which does not need any additional matching parts to find this optimal point.
...more
Nickel-Metal Hydride Batteries
This model simulates the discharge of a Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) battery using the Battery with Binary Electrolyte interface. The geometry is in one dimension and the model is isothermal. The model serves as an introduction to NiMH modeling, and can be further extended to include various side reactions.
...more
Mosfet Transistor
This model calculates the DC characteristics of a simple MOSFET. The drain current versus gate voltage characteristics are first computed in order to determine the threshold voltage for the device. Then the drain current vs drain voltage characteristics are computed for several gate voltages. The linear and saturation regions for the device can be identified from these plots.
...more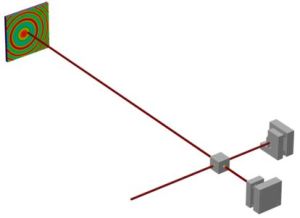
Michelson Interferometer
This model couples the Heat Transfer in Solids, Solid Mechanics and Geometrical Optics interfaces to compute the effect of thermal expansion of optical components on the interference pattern displayed by a Michelson interferometer.
...more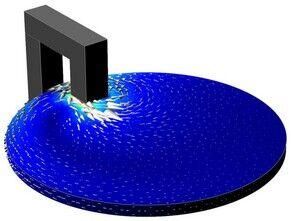
Magnetic Brake
A magnetic brake consists of a permanent magnet, which induces currents in a rotating copper disk. The resulting eddy currents interact with the magnetic flux to produce Lorentz forces and subsequently a braking torque. This 3D problem is solved using a stationary formulation for the electromagnetic field coupled to an ordinary differential equation for the rotational rigid body dynamics.
...more
Inductor Coil
This example models the deposition of an inductor coil in 3D. The geometry includes the extrusion of the deposition pattern into an isolating photoresist mask, and a diffusion layer on top of the photoresist. The mass transfer of copper ions in the electrolyte has a major impact on the deposition kinetics, resulting in higher deposition rates in the outer parts of the deposition pattern. The model is solved in a time-dependent study using a moving mesh.
...more
Induction Heaters
Induction heating is similar to the Joule Heating Effect, but with one important modification. The currents that heat the material are induced by means of electromagnetic induction; it is a noncontact heating process.By applying a high-frequency alternating current to an induction coil, a time-varying magnetic field is generated. The material to be heated, known as the workpiece, is placed inside the magnetic field, without touching the coil. Note that not all materials can be heated by induction, only those with high electrical conductivity (such as copper, gold, and aluminum, to name a few). The alternating electromagnetic field induces eddy currents in the workpiece, resulting in resistive losses, which then heat the material up.
...more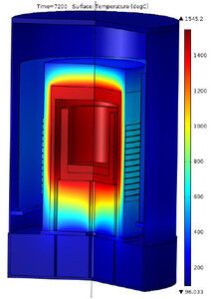
Induction Furnace
Induction furnaces are employed for vacuum distillation process to recover heavy metals after electro-refining operation. Induction furnace of suitable heating rate and cooled by passive means are required to be developed for this purpose. It is planned to set up a mock up induction furnace which will simulate the conditions to be realized in actual vacuum distillation furnace for this purpose. The mock-up facility will be used to demonstrate melting of 10 kg of copper in a graphite crucible and heated by induction furnace in a vacuum environment. The coil configuration and electrical parameters of the furnace are to be finalized to attain a temperature of about 1500 degC in 2 hours for the charge. Figure1 shows the schematic layout of the mock-up facility used. The furnace liner enclosing the crucible, essentially coupled with the magnetic field generated by coil, gets heated up and indirectly heats the crucible by radiation heat transfer. The melting of copper takes place in crucible. The copper liner prevents the coupling of stainless steel vessel with magnetic flux lines. The carbon felt insulation is used to prevent the heat loss to the coil and other parts. The stainless steel vessel encloses all the above parts. Thermal analysis of the mockup facility is being carried out using COMSOL Multiphysics code to optimize the various electrical parameters. First the Induction Heating Interface under the Heat Transfer Module of COMSOL Multiphysics was modeled and validated with the experimental data reported in the literature. The validated model was then used for 2D-axisymmetric transient thermal analysis of the mock-up facility.
...more
Inclined Screen
This model simulates the flow through a uniform inclined screen using the Screen feature in Single-Phase Flow physics and compares the results with an analytic solution.
...more
Horn Antenna
We provide a convenient 3D RF model of a generic pyramidal microwave horn, with a simple user-adjustable (parameterized) geometry. The model was prepared with Comsol Multiphysics v4.2a with the RF module. The user may specify the input waveguide size (width and height), horn flare length, horn aperture dimensions, and some other useful settings, all as global definitions. Computational region, meshes, and frequency range are then defined automatically (but can also be modified by the user). Two symmetry planes are employed to speed up the computation. The model computes the gain, VSWR, and E-plane and H-plane far-field beam patterns.
...moreBe first to Rate
Rate This