
Twin Shaft Paddle Blender
Paddles mounted on twin shafts in a ‘w’ shaped trough Normal filling level of material in the mixer is slightly above the shafts Overlapping motion and paddle design facilitates rapid fluidization and ensures excellent movement of particles Surplus space in the mixer trough to provide air around the particles so that they can move freely Twin shaft, counter-rotating paddles lift the particles in the centre of the mixer trough, in the fluidized zone, where mixing takes place in a weightless state Normal working volume is about 25 percent of the total volume of the trough Range of operation of the mixer is 40 to 140 percent of the rated capacity Peripheral speed ~100 metres per minute Mixing time can be as low as 1 minute. Mixing homogeneity of 98 – 99 percent. Choice of discharge valves including half bay doors, spherical disc valves are available. High speed choppers can be provided Rotating twin shaft paddle mixers are the most recent development.
...more
Rushton Turbine
The Rushton turbine is a disk type (six blade turbine) radial flow impeller. The diameter of the disk ranges from 66 to 75 percent of the internal vessel diameter. Impeller design is best suited for gas liquid contacting because of the circular disk. Gas is introduced through a sparger below the impeller; the disk directs the gas along a path of maximum liquid contact and prevents the gas from taking the direct vertical route along the mixer shaft Variant of the Rushton turbine is the Smith impeller in which the impeller blades are semi – circular or parabolic, instead of flat. For gas dispersion, the impeller shape allows for much higher power levels to be obtained in the process as compared to the Rushton turbine.
...more
Resin Mixer

Pitched Blade Turbine
Impeller Diameter – 450 mm to 3000 mm Hub with even number of blades are mounted at an angle of 10° to 90° with respect to the horizontal The most commonly used impeller of this type is the four bladed 45° pitched blade turbine Mixed flow impeller as fluid discharge has both axial and radial components Generally down-pumping Up-pumping in applications such as gas dispersions and floating solids mixing Used in flow control applications
...more
Open Blade Turbine
In open blade turbine, the blades are directly mounted on the hub. The number of blades may be two, four, six or eight. Two-blade paddle is generally used for solid suspension or blending applications requiring high flow and low shear. Paddles are normally operated at low speeds Coil impellers were developed for applications where solids frequently settle at the bottom of the vessel Spring design ensures that the impeller has adequate mechanical rigidity, strength to overcome the resistance offered by stiff solids during mixing operation
...more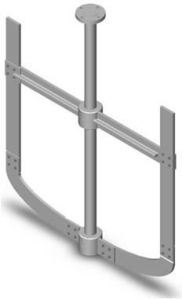
Low Clearance Impellers
The anchor impeller and the helical impeller are the two commonly used close clearance impellers. The diameter of the close clearance impellers is typically 90 – 95 percent of the inside diameter of the vessel. The shear near the vessel wall reduces the build up of stagnant material and promotes treat transfer. The anchor impeller is a radial flow impeller Helical impeller provides axial discharge of material by producing strong top to bottom motion Anchor blades may be used in combination with other types of impellers
...more
Hydrofoil Impeller
High efficiency impellers designed to maximize fluid flow and minimize shear rate. 3 or 4 tapering twisted blades, cambered and sometimes provided with rounded leading edges. The blade angle at the tip is lower than that at the hub. Resultant flow is streamlined. Vertices around the impeller are lower. Lower power number than PBT. The solidity ratio is the ratio of the total blade area to a circle circumscribing the impeller. Low solidity ratio – Liquid blending and solid suspensions. Higher solidity ratio – Axial flow patterns as the viscosity increases. In gas-liquid dispersions wide blades provide an effective area of preventing bypass of gas through the impeller hub.
...more
double planetary mixer
The double planetary mixer includes two blades that rotate on their own axes, while they orbit the mix vessel (also known as bowl) on a common axis. The mixer bowl may be jacketed for circulation of heating or cooling media. The mixer can be designed for operation under pressure or vacuum. Material is generally discharged by manual scooping of the material from the bowl. For extremely viscous materials, hydraulically operated automatic discharge systems are available that push the material out through the discharge valve
...more
Double Arm Kneader Mixer
Two mixing blades placed in a ‘w’ shaped horizontal trough Commonly used blade types are the sigma blade, masticator blade, spiral blade, shredder and naben blade Rotation of the blades is either tangential to each other or the blades may overlap within the trough. Blades pass the container walls and each other at close clearances generally (1-2 mm) The mixer bowl may be jacketed for circulation of heating or cooling media. Viscosity range upto 10 million cps Viscous mass of material is pulled, sheared, compressed, kneaded and folded by the action of the blades against the walls of the mixer trough. Fill Up is 40 – 65 % of bowl volume Mixing homogeneity upto 99 percent Specific power – 45 to 75 kW/ m3 Discharge of the material from the mixer By tilting of the mixer container Bottom discharge valve Through an extruder, screw
...moreBe first to Rate
Rate This