
3D Pelvis
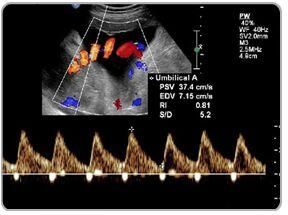
Uterine Artery Doppler Scans
Your baby needs plenty of nutrients and oxygen to grow at a healthy rate. Therefore, the walls of your uterine arteries should be stretchy, to allow as much blood through as possible. In pregnancy, these normally small arteries increase in size to allow more blood to reach your womb easily. This is called low resistance. If blood can’t get through to the placenta easily enough, your baby may not get the nutrients and oxygen he needs via the umbilical cord. Factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, hormone levels, and certain medications may increase the resistance in your artery walls.
...more
Sonohysterography
Saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS) or saline ultrasound uterine scan is a test where a small volume of saline (salt solution) is inserted into the uterus (or womb). This allows the lining of the uterus (endometrium) to be clearly seen on an ultrasound scan. It is also known as a saline ultrasound uterine scan. “Ultrasound” is the term used for an imaging test that uses high frequency soundwaves. SIS helps to see if there is any thickening of the endometrium of the uterus, or if there are polyps. Polyps are small growths of the endometrium. The scan can also be performed in the assessment of post menopausal endometrium or possible Asherman’s Syndrome (a condition caused by the presence of scars in the uterine cavity).
...more
Mammography Service
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breast. It can be used to check for breast cancer in women who have no signs or symptoms of the disease. It can also be used if you have a lump or other sign of breast cancer. Screening mammography is the type of mammogram that checks you when you have no symptoms. It can help reduce the number of deaths from breast cancer among women ages 40 to 70. Mammograms can sometimes find something that looks abnormal but isn't cancer. Mammograms are also recommended for younger women who have symptoms of breast cancer or who have a high risk of the disease. When you have a mammogram, you stand in front of an x-ray machine. The person who takes the x-rays places your breast between two plastic plates. The plates press your breast and make it flat. This may be uncomfortable, but it helps get a clear picture.
...more
Congenital Anomalies in 3d/4d Scan
3D scans show still pictures of your baby in three dimensions. 4D scans show moving 3D images of your baby, with time being the fourth dimension. It's natural to be really excited by the prospect of your first scan. But some mums find the standard 2D scans disappointing when all they see is a grey, blurry outline. This is because the scan sees right through your baby, so the photos show her internal organs. With 3D and 4D scans, you see your baby's skin rather than her insides. You may see the shape of your baby's mouth and nose, or be able to spot her yawning or sticking her tongue out. An anomaly scan, also known as a mid-pregnancy scan, takes a close look at your baby and your womb (uterus). The person carrying out the scan (sonographer) will check that your baby is developing normally, and look at where the placenta is lying. Although the anomaly scan is often called a 20-week scan, you may have it any time between 18 weeks and 20 weeks plus six days.
...more
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a prenatal test that allows your healthcare practitioner to gather information about your baby's health from a sample of your amniotic fluid. This is the fluid that surrounds your baby in the uterus. Amniocentesis is a prenatal test in which a small amount of amniotic fluid is removed from the sac surrounding the fetus for testing. The sample of amniotic fluid is removed through a fine needle inserted into the uterus through the abdomen, under ultrasound guidance. Why is an Amniocentesis Performed Amniocentesis is performed to confirm the presensce or absence of GENETICAL DEFECTS in the fetus which otherwise cannot be performed by any other method. Genetic defects such as Down Syndrome, Sickle cell disease, Cystic fibrosis...
...more
3D Pelvis
How is a pelvic ultrasound performed? most pelvic ultrasounds are performed using both the transabdominal and transvaginal approaches. Transabdominal ultrasound involves scanning through your lower abdomen. Transabdominal ultrasound usually provides an overview of the pelvis rather than detailed images. The transabdominal assessment is particularly helpful for the examination of large pelvic masses extending into the abdomen, which are not always well viewed with transvaginal ultrasound. A small amount of ultrasound gel is put on the skin of the lower abdomen, with the ultrasound probe then scanning through this gel. The gel helps improve contact between the probe and your skin.
...more
3D/4D ULTRASOUND
3D scans show still pictures of your baby in three dimensions. 4D scans show moving 3D images of your baby, with time being the fourth dimension. It's natural to be really excited by the prospect of your first scan. But some mums find the standard 2D scans disappointing when all they see is a grey, blurry outline. This is because the scan sees right through your baby, so the photos show her internal organs. With 3D and 4D scans, you see your baby's skin rather than her insides. You may see the shape of your baby's mouth and nose, or be able to spot her yawning or sticking her tongue out. 3D and 4D scans are considered as safe as 2D scans, because the images are made up of sections of two-dimensional images converted into a picture. However, experts do not recommend having 3D or 4D scans purely for a souvenir photo or recording, because it means that you are exposing your baby to more ultrasound than is medically necessary. Some private ultrasounds can be as long as 45 minutes to an hour, which may be longer than recommended safety limits.
...more
3D ultrasound

4D Ultrasound

Path Lab
Be first to Rate
Rate ThisOpening Hours